
在前面两章大家解读了动态数组、栈和队列的解读,这种最底层全是借助静态数据二维数组,靠 resize处理固定不动容积难题的,以前尽管客户见到的是动态数组,可是仍然应用的是静态数据二维数组,他是借助 resize 这一方式 处理 固定不动容积难题 ,可是大家今日要解读的 链表 不一样,链表是大家算法设计学习培训的一个关键,也是有可能是一个难题,为何链表那么关键呢?由于他是非常简单的也是 真真正正的动态性算法设计。
更深层次的了解引入(或是表针):和运行内存有关,尽管在 java 中大伙儿无需手动式的管理方法运行内存,可是对 链表 这类算法设计,更为深层次的了解,能够 协助大伙儿对引入、表针、乃至计算机软件中合代码优化有关的许多 话题讨论,有更为深层次的了解。
更深层次的了解递归算法:链表 原本也是有他十分清楚的递归结构的,、因为 链表 这类算法设计是 算法设计,我们可以更为 深层次了解递归算法,针对递归算法这类深层次理解是不能获得的。
链表 自身也是具备多功能性:輔助构成别的算法设计(hashMap 、栈和队列)
链表 是一种算法设计,在运行内存中根据 连接点纪录内存地址 而互相连接产生一条链的存储方法。对比二维数组来讲,链表在运行内存中不用持续的地区,只必须每一个连接点都可以 纪录下一个连接点 的 内存地址 ,根据 引入 开展搜索,那样的特性也就铸就了 链表 删改实际操作時间耗费不大,而搜索解析xml時间耗费非常大的特性。
大家日经常在 Java 中应用的 LinkedList 即是 双向链表。而在链表是由其基本上构成模块连接点 (Node) 来完成的。我们在日常中看到的链表绝大多数全是 单链表和双链表
模块连接点 (Node):
- class Node{
- E e;
- Node next;
- }
e 便是链表原素
next 指的是当今连接点的下一个连接点
针对 链表 而言它如同大家的列车一样,每一个连接点实际上便是一火车车厢,我们在车箱中储存真真正正的数据信息,而车箱和车箱中间也要开展联接,使我们数据信息是融合在一起的,客户能够 便捷的在全部的数据信息上开展查看或别的实际操作,那麼 数据信息和数据信息联接 便是由这一 next 来进行的
自然 链表 不可以数不胜数,假如一个连接点的 next 是 Null 了,就表明这一连接点是最后一个连接点了,这就是 链表
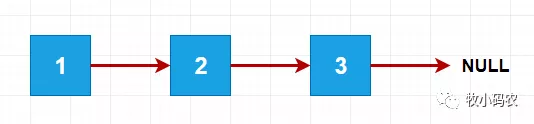
链表的优势:真真正正的动态性,不用解决固定不动容积的难题链表的缺陷:缺失了任意浏览的工作能力
在二维数组中:每一个数据库索引,立即从二维数组中取出数据库索引相匹配的原素,这是由于从最底层体制上,二维数组所开拓的室内空间,在运行内存里是持续遍布的,因此 我们可以立即能够 去找这一二维数组的偏位,立即测算出这一数据信息所储存的内存地址,能够 立即应用。
链表:而链表是靠 Next 一层一层联接的,必须依靠这一 Next 一点一点的去找大家必须取下来的原素。
- /**
- * 最底层链表的内部类
- * @param <E>
- */
- public class LinkedList<E> {
- //设计方案独享的内部类,针对客户而言不用了解链表最底层完成,
- // 不用了解node这一连接点,对客户屏蔽掉编号完成的最底层完成
- private class Node{
- public E e;
- public Node next;//public 能够 在LinkedList随便实际操作
- public Node(E e,Node next){
- this.e = e;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public Node(E e){
- this(e,null);
- }
- public Node(){
- this(null,null);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return e.toString();
- }
- }
- }
内部类Node:设计方案独享的内部类,针对客户而言不用了解链表最底层完成,不用了解node这一连接点,对客户屏蔽掉编号完成的最底层完成e:原素next:偏向Node的一个引入
以前大家讲的是怎样在二维数组中加上原素,我们在二维数组尾加上原素是十分便捷的,由于针对二维数组而言是次序排出的,有趣的是针对链表而言,正好相反,在链表头加上原素是十分便捷的,实际上那样很好了解,针对二维数组而言大家有 size 这一自变量,它立即偏向了二维数组中最后一个原素下一个部位,也就是下一个待加上原素的部位,因此 立即加上就很容易,由于有 size 这一自变量,在追踪二维数组的小尾巴,而针对链表而言大家开设了链表的一个头 head ,而沒有自变量来追踪链表的小尾巴,因此 我们在链表头加上原素是十分便捷的,最重要的便是 node.next = head 和 head = node,如下图所显示:
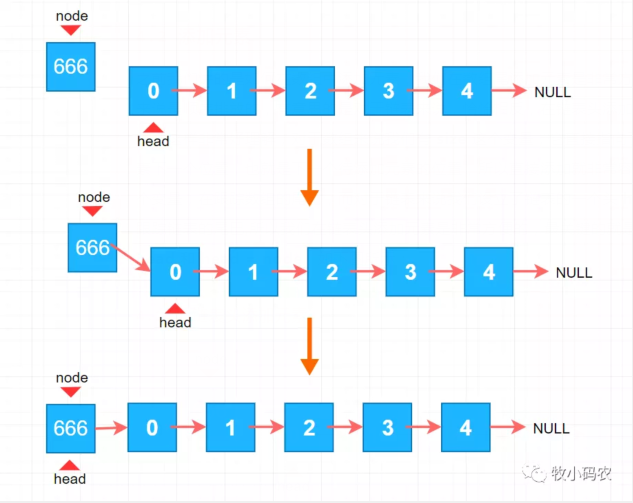
- //在链表头中加上原素e
- public void addFirst(E e){
- //方法一
- // Node node = new Node(e);
- // node.next = head;
- // head = node;
- //方法二
- head = new Node(e,head);
- size ;
- }
大家必须在数据库索引为2的地区加上原素 666,大家只必须寻找 原素666要 插进以前的连接点(1) ,大家管它叫 prev,随后把 以前连接点的(1) next 偏向 666,随后在将 666的这一 连接点偏向以前连接点(1) 的 以后的连接点(2) ,就完成了全部插入了,在其中重要编码便是 node.next=prev.next和prev.next=node;,在其中重要:我们要寻找加上连接点的前一个连接点 。

- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public void add(int index,E e){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
- if(index == 0)
- addFirst(e);
- else{
- Node prev = head;
- for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i ) {//将prev 放进下一个连接点,直至挪动到index - 1
- prev = prev.next;
- //方法一
- // Node node = new Node(e);
- // node.next = prev.next;
- // prev.next = node;
- //方法二
- prev.next = new Node(e,prev.next);
- size ;
- }
- }
- }
- //在链表结尾加上新的原素e
- public void addLast(E e){
- add(size,e);
- }
上边大家详细介绍了链表的加上实际操作,那麼我们在加上的情况下碰到了一个难题,便是在链表随意一个地区的情况下,加上一个原素,在链表头加上一个原素,与在链表别的地区加上原素,逻辑性上面有区别,为啥链表头加上原素会较为独特呢,由于我们在链表加上原素的全过程,要寻找待加上的 以前的一个连接点,可是因为针对链表头沒有以前的一个连接点,但是我们可以自身建立一个头节点,这一头连接点便是 虚似头节点,这一连接点针对客户而言是不会有, 客户也不会认知到这一连接点的存有,我们都是屏蔽掉这一连接点的存有,如下图所显示:
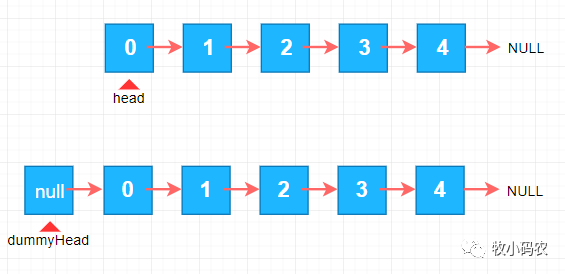
- private Node dummyHead;
- int size;
- public LinkedList(){
- dummyHead = new Node(null,null);
- size = 0;
- }
- //获得链表中的原素数量
- public int getSize(){
- return size;
- }
- //回到链表是不是为空
- public boolean isEmpty(){
- return size == 0;
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public void add(int index,E e){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
- Node prev = dummyHead;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- prev = prev.next;
- prev.next = new Node(e,prev.next);
- size ;
- }
- //在链表头中加上原素e
- public void addFirst(E e){
- add(0,e);
- }
- //在链表结尾加上新的原素e
- public void addLast(E e){
- add(size,e);
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public E get(int index){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- cur = cur.next;
- return cur.e;
- }
- //得到链表的第一个原素
- public E getFirst(){
- return get(0);
- }
- //获得链表的最后一个原素
- public E getLast(){
- return get(size - 1);
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public void set(int index,E e){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- cur = cur.next;
- cur.e = e;
- }
- //搜索链表中是不是有原素e
- public boolean contains(E e){
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- while (cur != null){
- if(cur.e.equals(e))
- return true;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }

加入团队要想删除索引为 (2) 部位的原素,大家必须寻找 待删掉连接点以前的一个部位,也就是(1) ,大家用 prev 表明,寻找这一连接点以后,那麼 (2) 便是大家必须删掉的数据库索引了 大家叫 delNode,如下图所显示:
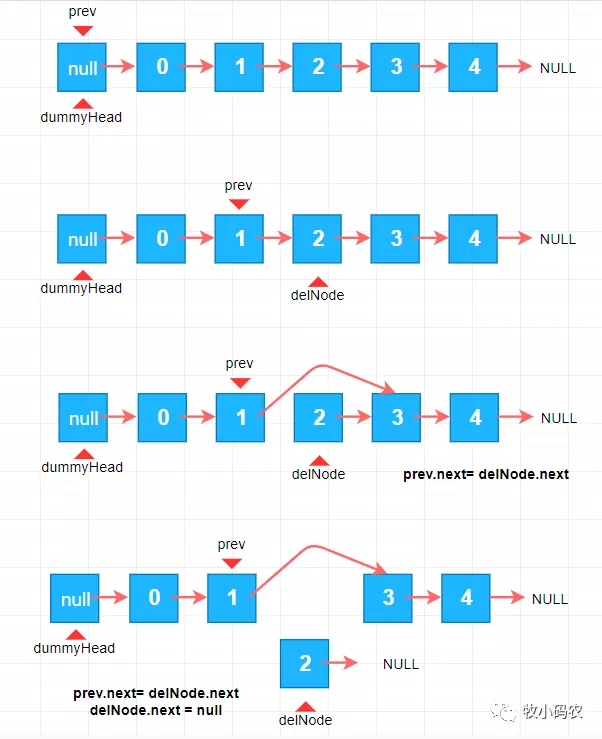
- //从链表中删掉Index(0-based)部位的原素,回到删掉的原素
- public E remove(int index){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Illegal index.");
- Node prev = dummyHead;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- prev = prev.next;
- Node retNode = prev.next;
- prev.next = retNode.next;
- retNode.next = null;
- size --;
- return retNode.e;
- }
- //从链表中删掉第一个部位的原素
- public E removeFirst(){
- return remove(0);
- }
- //从链表中删掉最后一个部位的原素
- public E removeLast(){
- return remove(size - 1);
- }
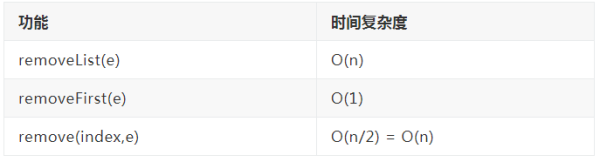
- /**
- * 最底层链表的内部类
- * @param <E>
- */
- public class LinkedList<E> {
- private class Node{
- public E e;
- public Node next;//public 能够 在LinkedList随便实际操作
- public Node(E e,Node next){
- this.e = e;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public Node(E e){
- this(e,null);
- }
- public Node(){
- this(null,null);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return e.toString();
- }
- }
- private Node dummyHead;
- int size;
- public LinkedList(){
- dummyHead = new Node(null,null);
- size = 0;
- }
- //获得链表中的原素数量
- public int getSize(){
- return size;
- }
- //回到链表是不是为空
- public boolean isEmpty(){
- return size == 0;
- }
- //在链表头中加上原素e
- public void addFirst(E e){
- //方法一
- // Node node = new Node(e);
- // node.next = head;
- // head = node;
- //方法二
- add(0,e);
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public void add(int index,E e){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
- Node prev = dummyHead;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- prev = prev.next;
- prev.next = new Node(e,prev.next);
- size ;
- }
- //在链表结尾加上新的原素e
- public void addLast(E e){
- add(size,e);
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public E get(int index){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- cur = cur.next;
- return cur.e;
- }
- //得到链表的第一个原素
- public E getFirst(){
- return get(0);
- }
- //获得链表的最后一个原素
- public E getLast(){
- return get(size - 1);
- }
- //在链表的index(0-based)部位加上新的原素e
- public void set(int index,E e){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- cur = cur.next;
- cur.e = e;
- }
- //搜索链表中是不是有原素e
- public boolean contains(E e){
- Node cur = dummyHead.next;
- while (cur != null){
- if(cur.e.equals(e))
- return true;
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
- //从链表中删掉Index(0-based)部位的原素,回到删掉的原素
- public E remove(int index){
- if(index < 0 || index > size)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Illegal index.");
- Node prev = dummyHead;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i )
- prev = prev.next;
- Node retNode = prev.next;
- prev.next = retNode.next;
- retNode.next = null;
- size --;
- return retNode.e;
- }
- //从链表中删掉第一个部位的原素
- public E removeFirst(){
- return remove(0);
- }
- //从链表中删掉最后一个部位的原素
- public E removeLast(){
- return remove(size - 1);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
- for (Node cur = dummyHead.next;cur != null; cur= cur.next)
- res.append(cur "->");
- res.append("Null");
- return res.toString();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
- //加上原素 0-4
- for (int i = 0; i < 5 ; i ) {
- linkedList.addFirst(i);
- System.out.println(linkedList);
- }
- //加上第二个原素加上 666
- linkedList.add(2,666);
- System.out.println(linkedList);
- //删掉第二个原素 666
- linkedList.remove(2);
- System.out.println(linkedList);
- //删掉第一个原素
- linkedList.removeFirst();
- System.out.println(linkedList);
- //删掉最后一个原素
- linkedList.removeLast();
- System.out.println(linkedList);
- }
- 0->Null
- 1->0->Null
- 2->1->0->Null
- 3->2->1->0->Null
- 4->3->2->1->0->Null
- 4->3->666->2->1->0->Null
- 4->3->2->1->0->Null
- 3->2->1->0->Null
- 3->2->1->Null
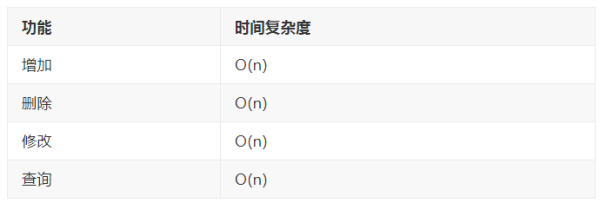
针对提升和删掉而言,如果是对链表头开展实际操作,那麼便是 O(1) 等级的复杂性,针对查看而言,也是一样
- /**
- * @program: Data-Structures
- * @ClassName Stack
- * @description:
- * @author: lyy
- * @create: 2019-11-20 21:51
- * @Version 1.0
- **/
- public interface Stack<E> {
- int getSize();
- boolean isEmpty();
- void push(E e);
- E pop();
- E peek();
- }
- import com.lyy.datasty.Mystack.Stack;
- //链表栈完成
- public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> {
- private LinkedList1<E> list;
- public LinkedListStack(){
- list = new LinkedList1<>();
- }
- @Override
- public int getSize() {
- return list.getSize();
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return list.isEmpty();
- }
- @Override
- public void push(E e) {
- list.addFirst(e);
- }
- @Override
- public E pop() {
- return list.removeFirst();
- }
- @Override
- public E peek() {
- return list.getFirst();
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
- res.append("Stack:top ");
- res.append(list);
- return res.toString();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedListStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ) {
- stack.push(i);
- System.out.println(stack);
- }
- stack.pop();
- System.out.println(stack);
- }
- Stack:top 0->Null
- Stack:top 1->0->Null
- Stack:top 2->1->0->Null
- Stack:top 3->2->1->0->Null
- Stack:top 4->3->2->1->0->Null
- Stack:top 3->2->1->0->Null
- /**
- * @program: Data-Structures
- * @ClassName Queue
- * @description:
- * @author: lyy
- * @create: 2019-11-21 21:54
- * @Version 1.0
- **/
- public interface Queue<E> {
- int getSize();
- boolean isEmpty();
- void enqueue(E e);
- E dequeue();
- E getFront();
- }
- public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E>{
- //设计方案独享的内部类,针对客户而言不用了解链表最底层完成,
- // 不用了解node这一连接点,对客户屏蔽掉编号完成的最底层完成
- private class Node{
- public E e;
- public Node next;//public 能够 在LinkedList随便实际操作
- public Node(E e, Node next){
- this.e = e;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public Node(E e){
- this(e,null);
- }
- public Node(){
- this(null,null);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return e.toString();
- }
- }
- private Node head,tail;
- private int size;
- public LinkedListQueue(){
- head = null;
- tail = null;
- size = 0;
- }
- @Override
- public int getSize() {
- return size;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return size == 0;
- }
- @Override
- public void enqueue(E e) {
- if(tail == null){
- tail = new Node(e);
- head = tail;
- }else{
- tail.next = new Node(e);
- tail = tail.next;
- }
- size ;
- }
- @Override
- public E dequeue() {
- if(isEmpty())
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
- Node retNode = head;
- head = head.next;
- retNode.next = null;
- if(head == null)
- tail = null;
- size --;
- return retNode.e;
- }
- @Override
- public E getFront() {
- if(isEmpty())
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("queue is empty.");
- return head.e;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
- res.append("Queue:front ");
- Node cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- res.append(cur "->");
- cur = cur.next;
- }
- res.append("Null tail");
- return res.toString();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ) {
- queue.enqueue(i);
- System.out.println(queue);
- if(i % 3 ==2){
- queue.dequeue();
- System.out.println(queue);
- }
- }
- }
- Queue:front 0->Null tail
- Queue:front 0->1->Null tail
- Queue:front 0->1->2->Null tail
- Queue:front 1->2->Null tail
- Queue:front 1->2->3->Null tail
- Queue:front 1->2->3->4->Null tail
- Queue:front 1->2->3->4->5->Null tail
- Queue:front 2->3->4->5->Null tail
- Queue:front 2->3->4->5->6->Null tail
- Queue:front 2->3->4->5->6->7->Null tail
- Queue:front 2->3->4->5->6->7->8->Null tail
- Queue:front 3->4->5->6->7->8->Null tail
- Queue:front 3->4->5->6->7->8->9->Null tail

- class Node{
- E e;
- Node next,prev;
- }
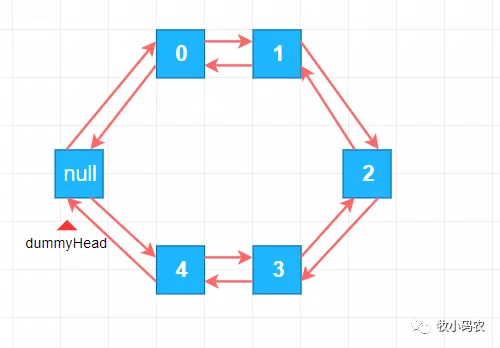
- class Node{
- E e;
- Node next,prev;
- }
在java中,LinkedList 最底层应用的便是 循环链表,也就是循环系统双向链表,到这儿大家链表就解读完成了。
